Cervical Cancer
Overview
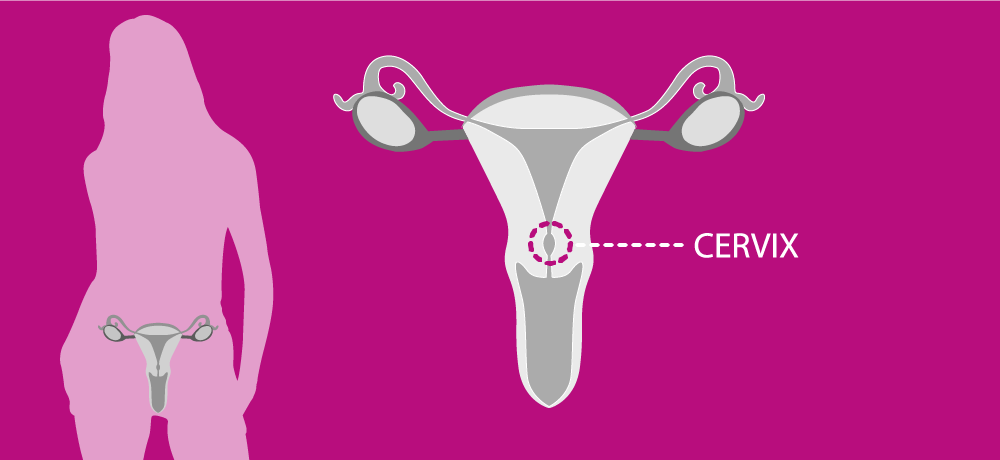
The cervix is the lower part of the womb (uterus), extending into the upper part of the vagina. Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women aged 15–44. The greatest incidence is observed in Central and Eastern Europe, where women have more than twice the risk of developing cervical cancer and more than three times the risk of dying from the disease compared with their Western European counterparts.
According to the European Commission and the European Network of Cancer Registries, approximately 30,447 women were diagnosed with cervical cancer in 2020, with approximately 13,437 associated deaths. Among European women of all ages, cervical cancer ranks as the eleventh most common cancer, with a lifetime risk of 1 in 111.
Europe ranks fourth in incidence and fifth in mortality worldwide for cervical cancer, compared with other continents. On average, more than 60% of women in Europe survive five years after a cervical cancer diagnosis. However, survival varies, with lower rates in Bulgaria, Latvia, Malta and Poland (below 60%) and higher rates in Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, the Netherlands, Slovenia and Sweden (around 70%).
For more information on cervical cancer, download the ENGAGe brochure What is cervical cancer or Gynaecological cancers in Europe (2024 update).
Symptoms
The symptoms of cervical cancer are not always obvious. Some patients may not notice any symptoms at all until the cancer has reached an advanced stage.
- Bleeding between periods
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Bleeding in postmenopausal women
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Smelly/bloody vaginal discharge
- Pelvic pain

Causes & risk factors
HPV infection is a recognized risk factor for developing cervical cancer. However, HPV infection is very common among sexually active people. So, having a positive cervical HPV DNA test doesn’t mean that you will develop cervical cancer. It does mean, however, that you must be regularly checked for this cancer. Your gynecologist can advise what types of test (colposcopy, cervical cytology) are available. In addition to HPV infection, other factors — such as your environment or your lifestyle choices may contribute to the development of cervical cancer. These include:
- Early sexual activity & many sexual partners
- Smoking
- Immunodeficiency, mostly HIV infection
- Skipping screenings (Pap smear, HPV test)
Diagnosis & prevention
The first step in finding cervical cancer is often an abnormal Pap test result. This will lead to further tests which can diagnose cervical cancer.
Vaccination
Vaccination is a part of primary prevention and is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity before you catch the virus. These vaccines are called prophylactic.
There are 3 different types of vaccine. The most powerful one - the 9-valent vaccine gives immunity against 7 high-risk and 2 low-risk types, which are responsible for the development of several genital warts and the majority of HPV-associated cancers.
Yes, the HPV virus may cause other cancers too! These cancers are harder to detect early compared to cervical cancers. They are anal, penile, vulvar, vaginal and oropharyngeal cancers.
Learn more details in our brochure Everything you need to know about the HPV vaccine.
Screening
There are 3 screening types:
- Cytology (PAP Smear): Its job is to show if there are any lesions in the cervix. If abnormal cells are detected in a Pap smear test, a biopsy is needed to confirm it. A cancer diagnosis cannot be made at this stage.
- HPV test: It shows if there is human papillomavirus in the cervix. None of those tests can confirm whether you have cancer or not.
- HPV self-sampling: This test can be performed at home individually and then sent directly to a laboratory.
Learn more details in our brochure Everything you need to know about the HPV tests.
Treatment
Cervical cancer treatment options include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or sometimes a combination of these.
Deciding treatment stratégy depends on several factors, such as the stage of the cancer, as well as age and overall state of health.
Treatment for early-stage cervical cancer, when the cancer remains within the cervix, has a good success rate and it is mostly treated with surgery only. If a cancer has spread from its original area, it is mostly treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy other than surgery.



