Ovarian Cancer
Overview
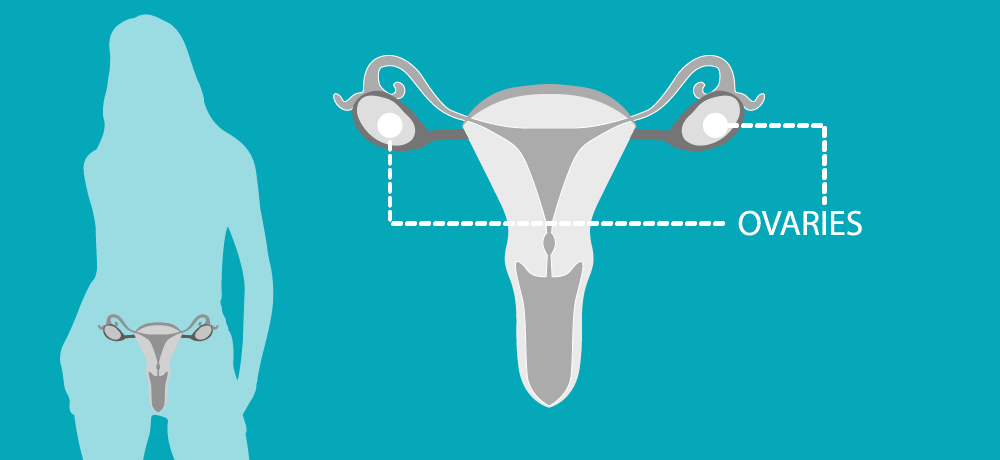
The ovaries are two oval-shaped glands located on either side of the uterus/womb and just below the opening of the fallopian tubes. They are responsible for producing eggs, or ‘ova’, and releasing the female sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone.
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, approximately 66,693 women were diagnosed with ovarian cancer in 2020, with approximately 44,053 associated fatalities. In Europe, ovarian cancer ranks as the eighth most common type of the disease and the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women.
In 2022, Europe recorded the highest rates of ovarian cancer incidence and mortality worldwide. These rates were notably higher in Central and Eastern Europe and lower in Southern Europe. A little less than 40% of women in Europe remain alive five years after being diagnosed with ovarian cancer. This survival rate is strongly influenced by the stage at which the cancer is
detected, with advanced-stage diagnoses often having poorer outcomes.
For more information on ovarian cancer download the ENGAGe brochure What is ovarian cancer or Gynaecological cancers in Europe (2024 update). If you are interested in PARP inhibitors, please scroll down to Tretament.
It’s so important to get trustworthy, accurate information about every step of your disease. Olivia is a comprehensive diginal ovarian cancer patient path and a single source of information for patients who have been diagnosed, being treated for and living with ovarian cancer, as well as their families, support networks and healthcare teams.
Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer may include:
- Feeling constantly bloated
- Nausea
- Abdominal (belly) swelling with weight loss
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Discomfort in the pelvis area
- A frequent need to urinate
- Constipation
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- Pain during sex
Risk factors
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is still unknown. However, doctors identified some factors that may increase a woman’s risk of getting it, such as:
- Age 50 or older
- Having a family history of ovarian cancer, breast cancer, or colorectal cancer (BRCA mutation)
- Estrogen hormone replacement therapy, especially with long-term use and in large doses
- Being overweight or obese
- Never having children
Diagnosis
If you have any signs or symptoms of ovarian cancer, you should ask your doctor about them
Before making a diagnosis, your doctor will:
- Ask about your symptoms and general health
- Check for any swelling or lumps in your abdomen
- Carry out an internal examination
- Ask about ovarian or breast cancer history in your family
- Take a blood sample
Treatment
The treatment for ovarian cancer depends on how far it has spread, your general health and whether you’re still able/willing to have children.
The most common treatments are surgery and chemotherapy.
Although there has been limited improvement in 5-year survival for most ovarian cancer patients over
the past three decades, the introduction of poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors as maintenance
therapy in ovarian cancer has resulted in improvements in progression-free survival and a trend toward
improved overall survival. For more information on PARP inhibitors please consult our brochure PARP inhibitors - a new treatment option for ovarian cancer.
Surgery
Almost all women with ovarian cancer need surgery. The aim is to remove all visible cancer .
Surgery usually involves removing at least:
- Both ovaries and the fallopian tubes
- The womb (a hysterectomy)
- A layer of fatty tissue in the abdomen (the omentum)
- All other tumor deposit. If cancer has spread throughout the abdomen, then bowel surgery may also be necessary.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (chemo) is the use of anti-cancer (cytotoxic) drugs to treat cancer. Most women with ovarian cancer have this therapy in addition to surgery.
It may be used:
- After surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells
- Before surgery to shrink the cancer and make it easier to remove afterwards
- If ovarian cancer comes back after initial treatment when upfront surgery is not an option
Nowadays, alongside a combination of surgery and chemotherapy, in case of advanced stage disease, a maintenance therapy either with oral or intravenus medications can be offered at the completion of primary treatment.




