Vaginal Cancer
Overview
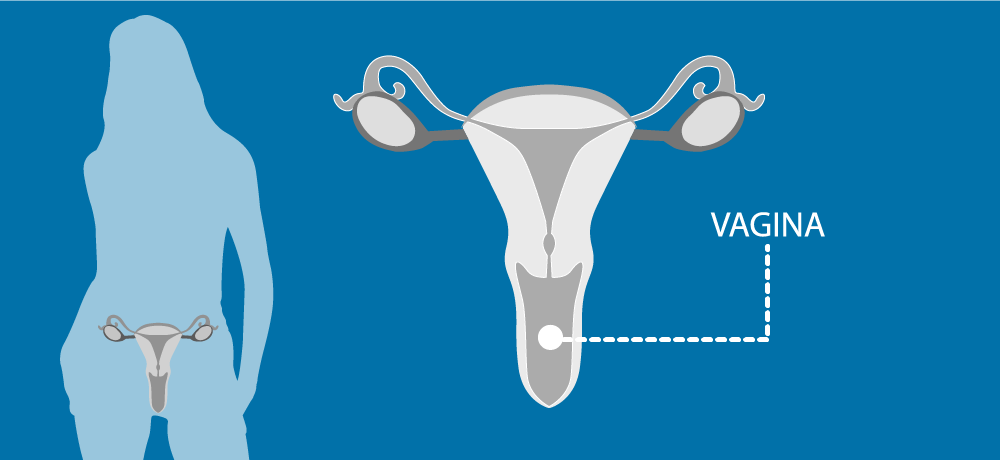
The vagina is a muscular passage linking the cervix (neck of the uterus) to the vulva (external genitals).
Primary vaginal cancer, a rare type of the disease that develops in the vagina, accounts for less than 1–2% of all genital cancers in women.
Vaginal cancer is often linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV) and other risk factors such as smoking, as well as to immunosuppression (decreased immunity states that can be attributed to certain diseases or drug-induced). This type of cancer is typically more common among older, postmenopausal women, but its incidence is rising in younger women due to HPV infections.
The most frequent histological subtype of vaginal cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, followed by adenocarcinoma. Melanomas, lymphomas and sarcomas are more rare. The cancer usually starts at the top part of the vagina, with its spread depending on location.
In 2022, according to the Global Cancer Observatory and the International Agency for Research on Cancer, Europe ranked fifth in vaginal cancer incidence and fourth in mortality compared with other continents. That same year, 2,947 women in Europe were diagnosed with the disease, with 1,267 associated deaths.
In Europe, the incidence and mortality of this type of cancer varies, being more common in Northern and Eastern Europe and less common in Southern Europe, possibly due to differences in the number of HPV infections and the availability of cervical screening programs.
Early diagnosis is crucial for survival from vaginal cancer, with a survival rate of 95% when detected early but significantly lower at advanced stages.
For more information, download the ENGAGe brochure on Vaginal Cancer, HPV tests or Gynaecological cancers in Europe (2024 update).
Symptoms
Early vaginal cancer may not cause any signs or symptoms. Symptoms of vaginal cancer include:
- Unusual vaginal bleeding, for example, after intercourse or after menopause
- Smelly or bloody vaginal discharge
- A lump or itch in your vagina that won’t go away
- Painful urination
- Constipation
- Pelvic pain
Risk factors
Researchers do not yet know the exact causes of vaginal cancer. They have, however, identified several risk factors for developing vaginal cancer.
These risk factors include:
- Older age. Most people who are diagnosed with vaginal cancer are older than 60.
- HPV infection.
- A history of cervical cancer.
- Smoking
- Early age at first intercourse
- HIV infection
Diagnosis
If you notice any signs of vaginal cancer, don't be afraid to ask your doctor about them.
Before a diagnosis, your doctor may:
- Ask about medications you are using
- Ask about your sexual experiences
- Ask about your family health history
- Look and feel for abnormalities in your pelvic area
- Take vaginal cytology to screen for HPV
Treatment
The main treatments for vaginal cancer are:
- Radiotherapy
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy



