Gynecological Cancers / Tumors & Testing

Being attentive to our health in combination with a healthy lifestyle is a key prevention strategy against gynecological cancers.
Scheduled screening procedures and testing can provide useful information on the risk of developing cancer. It can teach us steps we can take to reduce this risk. In some cases, the test outcomes could also help our doctors to choose the best treatment for a specific type of cancer.
Why is testing so important, both for secondary prevention and for the right treatment of gynecological cancers? Check out the brief summary below or download informational brochures about HPV tests and Genetic testing for women with cancer predisposing genes from ESGO ENGAGe.
Keep in mind the motto of World GO Day 2023 – GO for Testing. GO for Prevention. GO for the right Treatment. The perfect recipe for an active life!
Different types of screenings
The human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection affecting both women and men. Cervical cancer is a rare but dangerous complication of HPV.
The most important things we can do to help prevent this type of cancer is to get vaccinated against HPV virus, have regular screening tests starting at age 21, and go back to the gynecologist if our screening results are positive or abnormal.
Why are screenings important?
The task of screenings is to find the virus or pre-invasive early lesions soon so that there is no need for intervention. Or, if an intervention is necessary, to keep the treatment as minimal as possible.
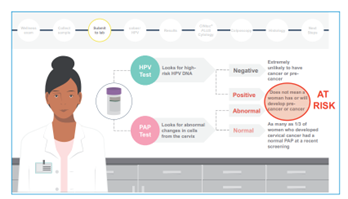
Pap tests (Pap smear) and HPV DNA tests (HPV test) are specific tests used by gynecologists during screenings for cervical cancer. HPV DNA tests can be also done individually at home using a self-collection kit.
Don´t forget! Screenings are important secondary prevention. They are not tests for cancer. They are tests to help prevent cancer.
Pap test (Pap smear)
What is a Pap test?
A Pap test, also called a Pap smear, is a procedure used to collect cells from the cervix – the lower, narrow end of uterus that’s at the top of the vagina.
Its job is to check the health of the cervix and to show if there are any abnormal cell changes or lesions. A lesion could be an inflammation, a problem caused by bacteria or fungus, or something more serious.
Detecting abnormal cells changes is the first step in halting the possible development of cervical cancer.
Who is a Pap test recommended for?
In general, doctors recommend beginning Pap testing at age 21 and repeating the testing every three years until you are 65.
If you’re older than 30, you can consider choosing a Pap/HPV co-test. Then Pap test and HPV test are done together, and the screening interval may increase to five years.
If you have some risk factors (e.g., a Pap smear that shows precancerous cells), the doctor may recommend more frequent Pap smears, regardless of age.
How is a Pap test done?
A Pap test is performed in a doctor’s office. It usually doesn´t hurt and takes only a few minutes.
During the procedure, the doctor gently inserts an instrument called a speculum into the vagina and then takes small samples of cells using a soft brush and a flat scraping device (spatula).
Sampled cells are sent to the laboratory and evaluated by a pathologist or cyto-technician, who is looking for an abnormal change or lesions.
The same or a second sample may be used also for detecting the presence of DNA of HPV virus.
What do the Pap tests results mean?
It can take up to three weeks until your gynecologist receives the lab results. You will be informed by your doctor when to get next Pap test or if you need further testing.
If only normal cervical cells were discovered during a Pap test, you’re said to have a negative result. This is good news. But keep in mind that new cell changes can still form on your cervix. That´s why you will still need to get regular Pap tests in the future.
If abnormal or unusual cells were discovered during a Pap test, you’re said to have a positive result. An abnormal Pap test doesn´t mean you have or will have precancer or cancer. But it does require careful follow-up with your doctor.
“Click for more information” buttons – like on FAQ page https://www.worldgoday.org/faq/
It’s not a test for cancer, it’s a test to help prevent cancer
HPV DNA test (HPV test) and HPV self-sampling
What is an HPV DNA test?
An HPV DNA test is a screening procedure used to look for the DNA of HPV virus (human papillomavirus) in the sample of cells from the cervix. Its job is to show if there is HPV virus on the cervix or not.
The test can be done by a doctor or you can perform it at home through a self-collection kit.
Various companies offer several types of HPV DNA tests. Some of them can detect all HPV types, while others detect only the two most important high-risk types (HPV 16 and HPV 18).
Knowing if you have a type of HPV that puts you at a high risk of cervical cancer is very important for several reasons. Based on the results, the doctor and patient can better decide on the next preventive steps – including follow-up monitoring, further testing, or treatment of abnormal cells. Being tested may also help stop the spread of the virus, because we can make lifestyle changes to protect others from getting HPV.
Who is HPV DNA test or self-sampling recommended for?
The age at which it is recommended to start HPV DNA testing varies by country – from 30 or 35 years of age. Depending on the local cancer numbers, screening may be also started earlier, at the age of 25.
The HPV DNA test is available only to women. While there is no approved test to detect the presence of virus in men, some doctors offer an anal Pap smear.
How is the HPV DNA test and self-sampling done?
The procedure is the same as in the case of a Pap test. During the HPV test, a small instrument called a speculum is gently inserted into the vagina. By doing so, the doctor can see the cervix and then obtain a small sample of cells.
After the procedure, the doctor can send sampled cells to a laboratory, where a specialist checks for the presence of HPV DNA. If you’re getting a Pap smear at the same time, the sample will be used for both tests.
You can also choose to perform the test individually at home based on the instructions on a self-kit and then send the swab or brush with the sample directly to the laboratory. The result of the test comes back to you, and you must call your gynecologist if it is positive.
What do HPV DNA tests and self-sampling results mean?
Results of the HPV DNA test will come back as positive or as negative.
A positive result of the test may mean that you have a high-risk type of HPV virus linked to cancer. It doesn´t mean that you have cancer right now. But it is a warning sign that there is a risk for developing cancer in the future. That´s why it is so important to visit your doctor and discuss the next steps.
If an HPV test is negative, the DNA of the HPV virus wasn´t found in the sample. Usually you can wait to re-test for 3 to 5 years.
“Click for more information” buttons – like on FAQ page https://www.worldgoday.org/faq/
Genetic Testing
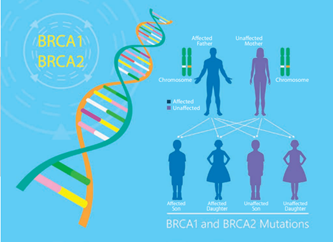
Most types of gynecological cancers occur by chance and are not inherited. A small number of them are caused by mutation in our genetic material, which may be passed down through families.
Half of our genes are inherited from our father and half from our mother. This means that if there is an error or alteration, in any gene (called a gene mutation), there is a 50% chance of passing this gene down to the next generation.
Why is genetic testing important?
Some of these gene mutations increase the risk of developing cancer. In the case of ovarian cancer, gene mutations can cause 15 – 20% of cases. The two genes most associated with this type of cancer are BRCA 1 and BRCA 2. Alteration in a gene can be responsible also for up to 3% of endometrial (womb) cancer.
Genetic testing is a procedure that identifies changes in genes, chromosomes, or proteins.
It may be used to identify increased risk of health problems, including cancer, to choose treatments or to assess responses to treatments.
Different countries, and sometimes also different hospitals in one country, offer genetic testing in different ways. In some of the health care systems, genetic counselling and testing can be done by treating clinician (medical oncologist, surgical oncologist, or clinical nurse specialist), in others, you will be referred to visit a genetic assessor, genetic counsellor or clinical geneticist.
The decision about whether to be tested or not is a complex one. Genetic testing has benefits as well as limitations and risks. You should discuss and carefully consider the choice before deciding to undergo the test.
Who is genetic testing recommended for?
Genetic testing has traditionally been offered to individuals with a strong family history of cancer. This usually means that several close relatives on the same side of the family have had a cancer associated with some gene mutation.
That´s why it is so important to learn the health history of our family members and share it with our doctors. Telling your doctor about family health history is the first step to find out if you may have a higher risk of cancer. It could help you and your doctor to decide what test you need to screen for cancer and also if genetic counselling or testing may be the right for you.
If someone in your close family has been found to carry a gene mutation, you can be offered genetic testing for that alteration. This is called predictive testing.
Using only family health history alone may miss identifying a number of gene carriers. Hence, genetic testing should be offered also to all women with ovarian and endometrial cancer.
How is genetic testing done?
Most genetic tests are using a blood sample, just like a routine blood test. DNA from the blood is then tested in the laboratory to find gene mutations.
In some cases, genetic testing can be also done from a sample of saliva or sample taken from the inside of your mouth (a buccal smear). Both of these tests are easy and safe, and they can be done at home with a kit. But it is important that testing is undertaken by an accredited laboratory.
Testing using a blood or saliva sample is called germline testing. Women who have developed ovarian cancer are also offered genetic testing of the tumor tissue, called somatic testing.
Only gene alterations found in the germline testing can be inherited.
What do genetic testing results mean?
In general, there are two main outcomes of genetic testing – a negative or positive test result.
A negative test result means that the laboratory doesn´t find any cancer-causing mutation in the genes. This finding can indicate that you are not a carrier of a specific genetic alteration or you do not have an increased risk of developing cancer.
A positive test result shows there is a (‘pathogenic’ or ‘likely pathogenic’) mutation in one of the genes that increases your cancer risk. This finding can lead to changing how you and your doctor manage your health care or treatment. It also supports the genetic testing of your relatives.
Genetic test results should be given to you by a trained professional. Don´t be afraid to talk to your doctor about the meaning of outcomes – both before and after the test is performed.
“Click for more information” buttons – like on FAQ page https://www.worldgoday.org/faq/
Genetic testing looks for changes in genetic material and its results help determine our risk of developing cancer during our lifetimes.
Knowing the risk enables us to discuss and make further reproductive and lifestyle choices. Test outcomes can also change the health care we or our family members receive – including medical prevention and the choice of the right treatment.